Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in muscle function, nerve regulation, blood pressure control, and bone health. During pregnancy, the body’s demand for magnesium increases as it supports fetal development reduces pregnancy discomforts and prevents complications. However, many pregnant women do not get enough magnesium, which can lead to cramps, fatigue, and even preterm labor risks.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Magnesium and Why Is It Important?
Magnesium is an essential mineral and electrolyte that helps regulate over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. It contributes to:
Energy production – Helps convert food into energy.
Muscle and nerve function – Prevents cramps, spasms, and nerve dysfunction.
Bone health – Strengthens bones and supports fetal skeletal development.
Cardiovascular function – Regulates blood pressure and prevents hypertension.
Hormonal balance – Reduces stress hormones and promotes relaxation.
Pregnant women require 350-400 mg of magnesium daily, as their bodies use this mineral at a higher rate to support fetal growth and overall maternal well-being.
How Magnesium Deficiency Affects the Body
A magnesium deficiency during pregnancy can cause a range of physical and emotional symptoms that affect both the mother and the developing baby.
1. Increased Muscle Cramps and Spasms
Magnesium helps regulate muscle contractions. A deficiency can lead to painful leg cramps, which are common in pregnancy.
Example: Many pregnant women experience charley horses (sudden, intense leg cramps), especially at night, due to magnesium depletion.
2. Higher Risk of Preterm Labor
Magnesium helps relax the uterus, preventing early contractions. A deficiency may increase the risk of preterm labor.
Example: Doctors often administer magnesium sulfate in hospitals to delay preterm birth.
3. Fatigue and Low Energy Levels
Magnesium supports energy production at the cellular level. Without enough magnesium, fatigue and sluggishness become common.
Example: A pregnant woman may feel exhausted despite adequate sleep as her body struggles to generate energy efficiently.
4. High Blood Pressure and Preeclampsia Risks
Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure. Low levels may contribute to hypertension and preeclampsia, a dangerous pregnancy complication.
Example: Women with magnesium deficiency may develop swelling, high blood pressure, and headaches, which are signs of preeclampsia.
5. Poor Sleep and Increased Stress Levels
Magnesium plays a role in nervous system regulation and stress management. Deficiency can lead to insomnia, anxiety, and irritability.
Example: A pregnant woman may struggle to fall asleep, feel overwhelmed, and experience mood swings due to low magnesium levels.
Benefits of Magnesium During Pregnancy
1. Reduces Leg Cramps and Muscle Pain
Magnesium relaxes muscles, reducing the frequency and severity of leg cramps.
Example: Women who take magnesium supplements or eat magnesium-rich foods often report fewer nighttime cramps.
2. Supports Fetal Development and Bone Strength
Magnesium is essential for the baby’s growing bones and teeth. It also prevents the mother’s bones from weakening.
Example: Mothers with sufficient magnesium intake are less likely to experience bone density loss postpartum.
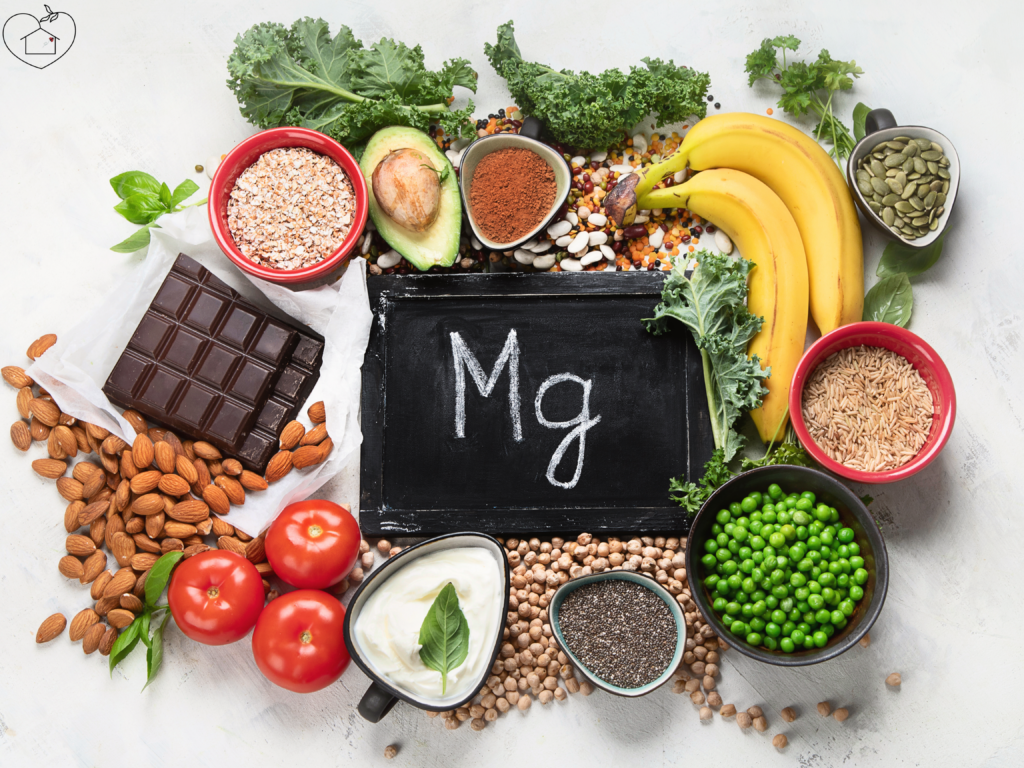
3. Helps Control Blood Sugar and Reduces Gestational Diabetes Risk
Magnesium plays a role in glucose metabolism and insulin regulation, lowering the risk of gestational diabetes.
Example: Women with high magnesium intake have better blood sugar control during pregnancy.
4. Lowers Stress, Anxiety and Improves Sleep
Magnesium calms the nervous system, helping pregnant women sleep better and manage stress more effectively.
Example: A magnesium supplement before bedtime can help an anxious mother relax and sleep deeper.
5. Prevents Constipation and Improves Digestion
Magnesium draws water into the intestines, softening stool and preventing constipation.
Example: Pregnant women who increase their magnesium intake report fewer digestive problems.
Best Magnesium-Rich Foods for Pregnancy
Eating whole foods rich in magnesium is the safest and most effective way to increase magnesium intake during pregnancy.
1. Leafy Green Vegetables
Spinach, kale, Swiss chard
Why It’s Important: These greens provide fiber, iron, and folate, which are essential for pregnancy.
2. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, pumpkin seeds, cashews, sunflower seeds
Why It’s Important: They provide healthy fats, protein, and magnesium to support energy levels.
3. Whole Grains
Brown rice, quinoa, oats
Why It’s Important: They are rich in fiber, magnesium, and B vitamins for sustained energy.
4. Bananas and Avocados
They contain natural electrolytes, preventing cramps and promoting hydration
5. Dark Chocolate (70% Cocoa and Above)
It’s a delicious source of magnesium, plus it improves mood and reduces stress.
Magnesium during pregnancy supports both maternal and fetal health, preventing complications like muscle cramps, stress, preterm labor, and gestational diabetes. Providing sufficient magnesium intake through food sources or supplements can make a significant difference in overall well-being. Always consult your healthcare provider before adding supplements, and prioritize magnesium-rich foods for a healthy pregnancy.
Watch and Read!
- “Real Food for Pregnancy” by Lily Nichols
- “The Mama Natural Week-by-Week Guide to Pregnancy and Childbirth” by Genevieve Howland
- “Expecting Better” by Emily Oster
- “What to Expect When You’re Expecting” (2012)
- “Away We Go” (2009)
- “Baby Boom” (1987)
FAQs
Yes, but always consult your doctor to determine the right dosage and type of magnesium.
Magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate are the most recommended forms for absorption and digestion.
Excessive magnesium can cause diarrhea, nausea, and low blood pressure, so always take the recommended dose.